In the dynamic landscape of modern IT infrastructure, the concept of virtualization has become a cornerstone for efficient server management. Virtualization technology has revolutionized the way servers operate, enabling organizations to maximize resource utilization, enhance scalability, and streamline maintenance. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of virtualization, its benefits, and how it plays a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of contemporary server management.
What is Virtualization?
At its core, virtualization is the process of creating a virtual (rather than physical) version of something, whether it’s an operating system, server, storage device, or network resource. In the context of server management, we primarily focus on server virtualization.
Server Virtualization: Server virtualization involves dividing a physical server into multiple virtual machines (VMs), each capable of running its own operating system (OS) and applications. This is achieved through a hypervisor, which is a software layer that sits between the hardware and the operating systems. The hypervisor allocates resources and manages the interactions between the VMs and the underlying hardware.
Key Components of Virtualization:
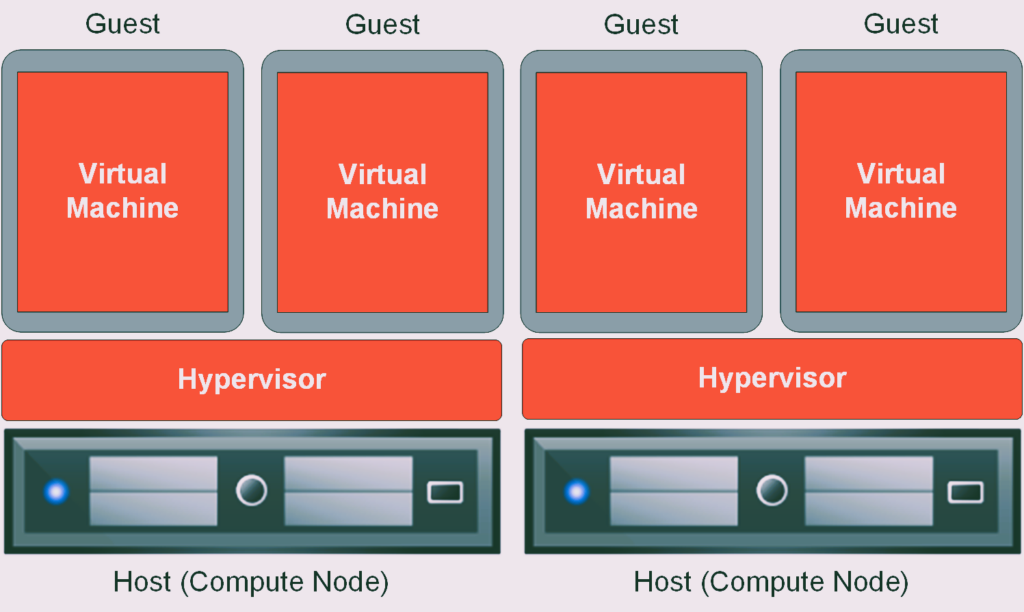
- Hypervisor: The hypervisor, also known as a Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM), is a critical component of virtualization. It abstracts and isolates the operating systems from the physical hardware, enabling multiple VMs to run independently on a single physical server.
- Virtual Machine (VM): A VM is an emulation of a computer system within a virtual environment. It includes a virtualized set of hardware, an operating system, and applications. Multiple VMs can coexist on the same physical server, each operating independently.
- Host Machine: The host machine is the physical server that runs the hypervisor and hosts multiple VMs. The resources of the host machine, such as CPU, memory, and storage, are allocated among the VMs.
- Guest Operating System: Each VM runs its own guest operating system, which can be different from the host operating system. This flexibility allows for a diverse range of applications and environments to coexist on the same physical server. Read about the game-changing trends in the gaming industry in 2023.
Benefits of Server Virtualization:
- Resource Utilization: Virtualization allows for more efficient use of hardware resources. Multiple VMs can run on a single physical server, maximizing its capacity and reducing hardware sprawl.
- Cost Savings: By consolidating workloads onto fewer physical servers, organizations can achieve significant cost savings in terms of hardware, power consumption, and cooling requirements.
- Scalability: Virtualization provides scalability by enabling the easy creation and deployment of additional VMs. This flexibility is particularly valuable for businesses experiencing growth or fluctuating resource demands.
- Isolation and Security: VMs are isolated from each other, enhancing security. If one VM encounters an issue or is compromised, it doesn’t affect the others. Additionally, snapshots and backups can be easily created for VMs, facilitating data recovery.
- Ease of Management: Virtualization simplifies server management tasks. Tasks such as provisioning new servers, migrating VMs between hosts, and adjusting resource allocations can be performed with ease through management interfaces.
- High Availability: Virtualization enables features like live migration, allowing VMs to be moved between hosts without downtime. This ensures high availability and minimizes service interruptions during maintenance or hardware failures.
Popular Virtualization Solutions:
- VMware vSphere: VMware is a leading provider of virtualization solutions. vSphere is a comprehensive platform that includes a hypervisor, management tools, and features for high availability and workload balancing.
- Microsoft Hyper-V: Hyper-V is Microsoft’s hypervisor-based virtualization platform. It is integrated into Windows Server and provides features for creating and managing VMs.
- KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine): KVM is a Linux kernel module that enables the host machine to function as a hypervisor. It is widely used in open-source virtualization solutions.
- Citrix Hypervisor (formerly XenServer): Citrix Hypervisor is an enterprise-class virtualization solution that offers advanced features such as live migration, resource pooling, and workload balancing.
Future Trends in Virtualization:

- Containerization: Containerization technologies, such as Docker and Kubernetes, are gaining prominence alongside virtualization. Containers offer lightweight, portable, and scalable solutions for application deployment.
- Edge Virtualization: With the rise of edge computing, virtualization is extending to the edge of networks. Edge virtualization enables the deployment of VMs closer to end-users, reducing latency and improving performance.
- AI-driven Automation: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into virtualization platforms is enhancing automation capabilities. This trend aims to optimize resource allocation, improve security, and streamline management tasks.
Platforms for Staying Informed:
To stay informed about the latest trends and insights into virtualization, platforms like GameSpot can offer valuable perspectives. While primarily focused on gaming, these platforms often cover broader technology topics, including virtualization, providing a comprehensive view of industry developments.
Conclusion: The Evolution of Server Management with Virtualization:
Virtualization has transformed server management, offering organizations unprecedented flexibility, efficiency, and scalability. As technology continues to advance, the integration of virtualization with emerging trends like containerization and edge computing promises even greater possibilities. Understanding the principles and benefits of virtualization is essential for IT professionals and organizations seeking to optimize their infrastructure and adapt to the evolving demands of the digital landscape. Embrace the power of virtualization, stay informed, and pave the way for a future of efficient and resilient server management.


